Yin Yang - 阴阳 - 陰陽
Where does the Yin Yang Symbol come from?
|
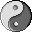 is a well-known Chinese Yin Yang symbol. Sometimes it's called Tai-Chi symbol. The Tai-Chi is from I-Ching. The I-Ching is the greatest foundation of Chinese philosophy. It’s development is from the natural phenomena of our universe. Because I-Ching comes from nature, it should be easy.
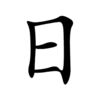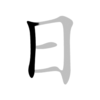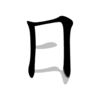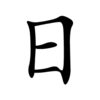
The Chinese characters of I-Ching (易经 - 易經) are 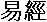 . The second character means a book, a profound book. The first character means ease or change. Since I-Ching is easy, some people call it as "The Book of Ease" or "The Book of Changes".
The original Chinese character of 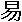 is 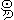 , which is a symbol combining the sun (top) and moon (bottom). It's easy for people to understand the philosophy by talking about the sun (Yang), moon (Yin) and universe. After observing the universe, ancient Chinese found that the universe is changing every day. Although it changes easily every day, it also has seasonal and annual cycles. From these cycles the unchanging rules are created. However, it's not easy to use the 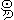 method to find the unchanging rules from the universe and apply on human activities. That's why some people think I-Ching is easy and some don't.
 The Dipper at night
The Dipper at night | By observing the sky, recording the Dipper's positions and watching the shadow of the Sun from an 8-foot (Chinese measurement) pole, ancient Chinese determined the four directions. The direction of sunrise is the East; the direction of sunset is the West; the direction of the shortest shadow is the South and the direction of the longest shadow is the North. At night, the direction of the Polaris star is the North.
They noticed the seasonal changes. When the Dipper points to the East, it's spring; when the Dipper points to the South, it's summer; when the Dipper points to the West, it's fall; when the Dipper points to the North, it's winter. |
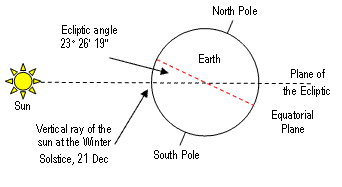
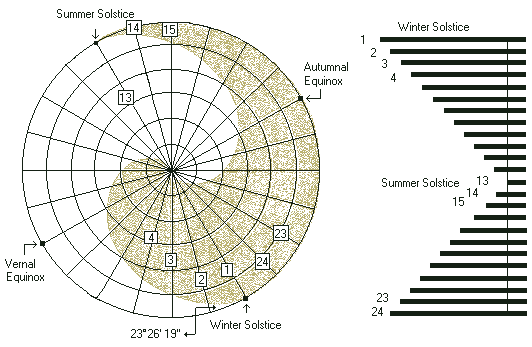
When observing the cycle of the Sun, ancient Chinese simply used a pole about 8 feet long, posted at right angles to the ground and recorded positions of the shadow. Then they found the length of a year is around 365.25 days. They even divided the year's cycle into 24 Segments, including the Vernal Equinox, Autumnal Equinox, Summer Solstice and Winter Solstice, using the sunrise and Dipper positions.
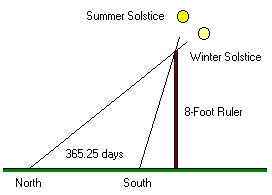
They used six concentric circles, marked the 24-Segment points, divided the circles into 24 sectors and recorded the length of shadow every day. The shortest shadow is found on the day of Summer Solstice. The longest shadow is found on the day of Winter Solstice. After connecting each lines and dimming Yin Part from Summer Solstice to Winter Solstice, the Sun chart looks like below. The ecliptic angle 23 26' 19'' of the Earth can be seen in this chart.
 | The Ecliptic is the Sun's apparent path around the Earth.
It's tilted relative to the Earth's equator.
The value of obliquity of the Ecliptic is around 23 26' 19'' in year 2000. |
By rotating the Sun chart and positioning the Winter Solstice at the bottom, it will look like this  . The light color area which indicates more sunlight is called Yang (Sun). The dark color area has less sunlight (more moonlight) and is called Yin (Moon). Yang is like man. Yin is like woman. Yang wouldn't grow without Yin. Yin couldn't give birth without Yang. Yin is born (begins) at Summer Solstice and Yang is born (begins) at Winter Solstice. Therefore one little circle Yin is marked on the Summer Solstice position. Another little circle Yang is marked on the Winter Solstice position. These two little circles look like two fish eyes.
In general, the Yin Yang symbol is a Chinese representation of the entire celestial phenomenon. It contains the cycle of Sun, four seasons, 24-Segment Chi, the foundation of the I-Ching and the Chinese calendar.
© Copyright 1999-111 Allen Tsai
|
|

易 - Yì
易经 Yì jīng
The Ecliptic is the Sun's apparent path around the Earth.
It's tilted relative to the Earth's equator.
The value of obliquity of the Ecliptic is around 23 26' 19'' in year 2000.
 Chinese Yin Yang Tai-Chi Symbol Chinese Yin Yang Tai-Chi Symbol
|
By observing the cycle of the Sun, we can use a pole, post at right angles to the ground and record the lengths of the shadow about every 15 days for a year. The shortest shadow is found on the day of Summer Solstice in China. The longest shadow is found on the day of Winter Solstice. The day of Winter Solstice has the least sunshine in the year. After Winter Solstice, the day will gain more sunshine each day till Summer Solstice. We can say Yang begins right after Winter Solstice and Yin begins right after Summer Solstice in the northern hemisphere.
After recording 24 shadow lines, we move the lines into the diagram of six concentric circles with 24 sectors beginning from Winter Solstice to Summer Solstice. The length of each line will subtract the portion of the length of Summer Solstice shadow line because we want to give Summer Solstice maximum Yang.
From Winter Solstice to Summer Solstice, the shadow lines are drawn from the center of the circle to the boundary. From Summer Solstice to Winter Solstice, the shadow lines are drawn from circle boundary to the center, because ancient Chinese believed that Chi Energy goes different directions right after Summer Solstice and Winter Solstice.
Next, we can connect all the lines and dim the shadow lines (Yin) part, the Ying Yang symbol appears.  .
© Copyright 1999-111 Allen Tsai
|
|
24 Posisi Matahari - 24 Solar Terms - 二十四节气 - 二十四節氣
|
24 Solar Terms - 二十四节气 - 二十四節氣
Dalam kalender lunisolar Asia Timur, satu tahun dibagi menjadi 24 (二十四) posisi matahari (SOLAR TERMS - 节气 - 節氣) berdasarkan pembagian ekliptika (lintasan yang dilalui matahari seperti terlihat dari bumi) menjadi 24 bagian dengan jarak 15° satu sama lainnya. Dalam pembagian satu tahun menjadi 4 musim, setiap musim dibagi menjadi 6 posisi matahari (QI - 气 - 氣) yang masing-masing lamanya 15 hari. Dari total 24 posisi matahari, 12 posisi matahari disebut zhongqi (中气 - 中氣) dan 12 posisi matahari disebut jieqi (节气 - 節氣). Setiap posisi matahari diberi nama yang melambangkan fenomena alam dan musim. Sistem ini diadopsi di Korea, Jepang, dan Vietnam dengan memakai istilah yang sama.
|
|


















Tidak ada komentar:
Posting Komentar